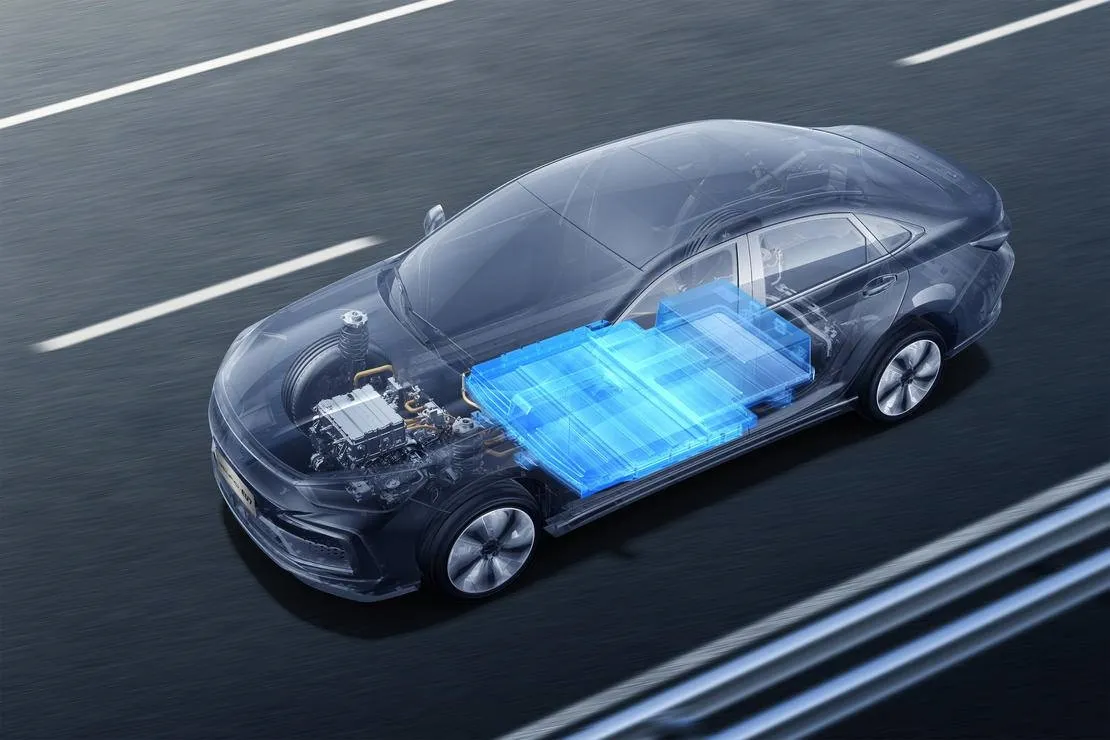
Power batteries provide electric drive for new energy vehicles. They are not only heavy and complex in structure, but their performance is directly related to the vehicle's range, safety and power. They also largely affect the manufacturing cost of the vehicle. This article will take you to learn more about the structure and core components of power batteries. Let's learn together
Battery life is divided into calendar life and cycle life:
1.Calendar life is determined by storage time rather than usage time. Calendar life refers to how long the battery will last if it is not used. Typically, calendar life is between 8 and 15 years, depending on the quality of the battery and the environment in which it is used. For general-purpose lithium-ion batteries, the calendar life may be even longer, reaching 15 to 20 years.
Experimental studies have found that the key factors affecting the calendar life of batteries are the remaining power and the ambient temperature. This experiment conducted a 700-day attenuation test on the calendar life of two batteries with SOC remaining power of 15% and 90% at ambient temperatures of 25 degrees and 35 degrees respectively. The test results show that the battery with an ambient temperature of 25 degrees and a SOC remaining power of 15% has the highest battery capacity retention rate after 700 days; followed by the battery with an SOC of 15% at 35 degrees; then the battery with an SOC of 90% at 25 degrees; and finally the battery with an SOC of 90% at 35 degrees. This shows that the SOC remaining power has a great impact on the battery calendar life, and it will be higher than the impact of the ambient temperature. Therefore, when our vehicles are stored for a long time, try not to keep the remaining power very high. In order to obtain the best shelf life, the storage power of lithium-ion batteries should be 40-50%.
2. Cycle life refers to the number of times a battery is charged and discharged. One cycle is when the battery is fully charged from 0% to 100% and then used up. If the battery is charged from 50% to 100% and then used up again, it is counted as 0.5 cycles. In other words, multiple charge and discharges totaling 100% is considered a complete cycle. Currently, the common lithium iron phosphate battery can generally be used 4,000 times, while ternary lithium batteries can generally be used more than 2,000 times.
Experimental studies have found that the key factors affecting the calendar life of batteries are the remaining power and the ambient temperature. This experiment conducted a 700-day attenuation test on the calendar life of two batteries with SOC remaining power of 15% and 90% at ambient temperatures of 25 degrees and 35 degrees respectively. The test results show that the battery with an ambient temperature of 25 degrees and a SOC remaining power of 15% has the highest battery capacity retention rate after 700 days; followed by the battery with an SOC of 15% at 35 degrees; then the battery with an SOC of 90% at 25 degrees; and finally the battery with an SOC of 90% at 35 degrees. This shows that the SOC remaining power has a great impact on the battery calendar life, and it will be higher than the impact of the ambient temperature. Therefore, when our vehicles are stored for a long time, try not to keep the remaining power very high. In order to obtain the best shelf life, the storage power of lithium-ion batteries should be 40-50%.
2. Cycle life refers to the number of times a battery is charged and discharged. One cycle is when the battery is fully charged from 0% to 100% and then used up. If the battery is charged from 50% to 100% and then used up again, it is counted as 0.5 cycles. In other words, multiple charge and discharges totaling 100% is considered a complete cycle. Currently, the common lithium iron phosphate battery can generally be used 4,000 times, while ternary lithium batteries can generally be used more than 2,000 times.
Professor Ouyang Minggao, an academician of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and Tsinghua University, published a paper entitled "Key Issues in the Attenuation Process of Lithium-ion Batteries Throughout Their Life Cycle". The experimental results in the paper show that different DOD discharge depths will significantly affect the battery's cycle life, and higher DOD will accelerate battery attenuation. Experiments show that if only 40% of the power is used after each charge, the DOD is 40%, and the battery is charged to 90% and recharged when it is 50% used. Under this usage condition, the cycle life of a battery can reach 7994 times. The experiment is to charge 80% each time and recharge when it is 20% used, that is, the DOD discharge depth is 60%. The battery cycle life under this usage method is 2576 times, which is only about one-third of the former. This shows that shallow charging and shallow discharging is the important way to extend the life of power batteries.
Summary:
Factors affecting the calendar life of lithium batteries
1. Battery quality: High-quality lithium batteries use high-quality materials and advanced production processes, and their performance is more stable and their life is longer.
2. Ambient temperature: High temperature will accelerate the chemical reaction inside the battery, causing the battery performance to decay.
3. Battery status: The battery's charge and discharge status, charge retention ability, etc. will affect its life.
4. Usage and maintenance methods
How to extend the calendar life of lithium batteries1. Battery quality: High-quality lithium batteries use high-quality materials and advanced production processes, and their performance is more stable and their life is longer.
2. Ambient temperature: High temperature will accelerate the chemical reaction inside the battery, causing the battery performance to decay.
3. Battery status: The battery's charge and discharge status, charge retention ability, etc. will affect its life.
4. Usage and maintenance methods
1. Choose high-quality battery products: Choose well-known brands and battery products with guaranteed quality when purchasing.
2. Maintain a suitable ambient temperature: Try to avoid working the battery in high temperature or extremely cold environments to reduce performance decay.
3. Reasonable use of batteries: Follow the correct charge and discharge strategy to avoid damage to the battery caused by excessive charge and discharge.
4. Regular maintenance: Check and maintain the battery regularly to detect and solve potential problems in time.
2. Maintain a suitable ambient temperature: Try to avoid working the battery in high temperature or extremely cold environments to reduce performance decay.
3. Reasonable use of batteries: Follow the correct charge and discharge strategy to avoid damage to the battery caused by excessive charge and discharge.
4. Regular maintenance: Check and maintain the battery regularly to detect and solve potential problems in time.
 +86 13332949210
+86 13332949210 info@xihobattery.com
info@xihobattery.com







 Xiho
Xiho Jan 05 2025
Jan 05 2025